XML Transformations (XSLT) — Part II
XML Foundations (INFOSYS 242)
Erik Wilde, UC Berkeley iSchool
Tuesday, September 26, 2006
|
|
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons |
|
|
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons |
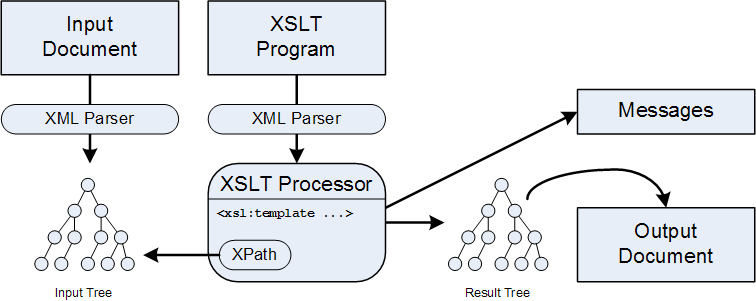
XSLT processes documents by matching nodes in the document tree to templates, which then are executed to process these nodes. This process of matching and executing templates is the core of XSLT's processing model. XSLT has built-in templates which complement the user-supplied templates, so that the XSLT processor always finds a template to execute. Templates can conflict, and it is then necessary to resolve this conflict by finding the best match
of all matching templates. This conflict resolution process also is a very important component of the XSLT processing model.
spaghetti code
applied)
<xsl:template match="*"> <xsl:text>( Element:</xsl:text> <xsl:value-of select="local-name()"/> <xsl:apply-templates select="* | @*"/> <xsl:text>)</xsl:text> </xsl:template> <xsl:template match="@*"> <xsl:text>Attribute: </xsl:text> <xsl:value-of select="local-name()"/> </xsl:template>
*trthead/trp[@class='warning']warning|<xsl:template match="* | /"> <xsl:apply-templates/> </xsl:template>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"> </xsl:stylesheet>
<xsl:template match="text() | @*"> <xsl:value-of select="."/> </xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="processing-instruction() | comment()"/>
besttemplate must be found
00.25-0.250.5<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"> <xsl:template match="/"> <xsl:apply-templates select="descendant::a"/> </xsl:template> <xsl:template match="*"/> <xsl:template match="a"/> <xsl:template match="b/a"/> <xsl:template match="c/b/a"/> </xsl:stylesheet>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <c> <b> <a/> </b> </c>
| Pattern | Priority | Resolution Step | Manual Adjustment |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
Built-in: |
✓ | ✓ | |||||
Built-in: |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
|
-0.5 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
|
0.0 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
|
0.25 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
|
0.25 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | priority="1" |
-0.5 and 0.50.5overwritingtemplates, the behavior can be customized